Did You Know?
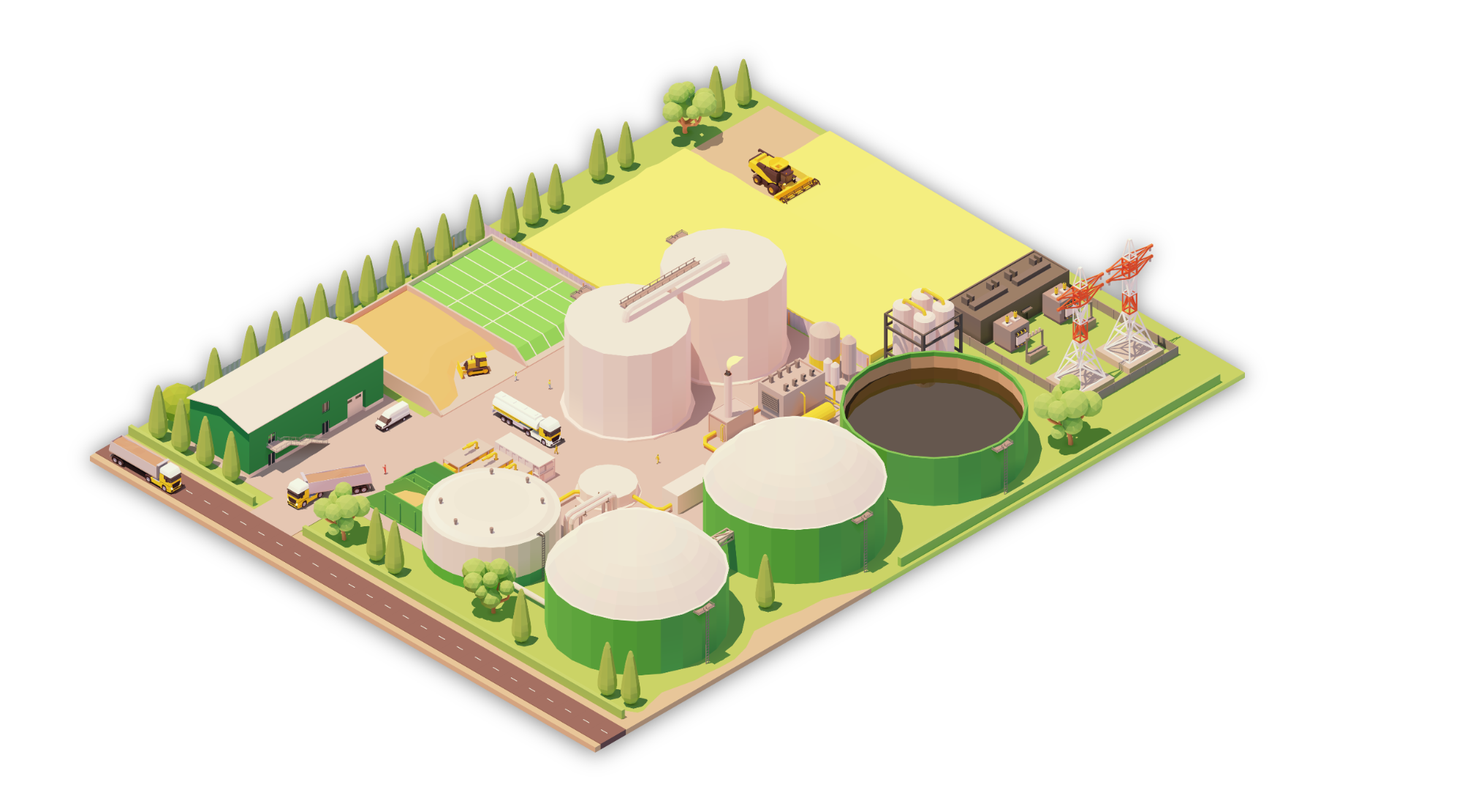
Biogas Production Facilities

DID YOU KNOW ABOUT ANAEROBIC DIGESTION?
According to the European Biogas Association (EBA, Annual Report 2021), the number of anaerobic digestion facilities at EU level is around 19000 and produce 18 billion cubic meters (bcm) of methane equivalent per year. These facilities play an important role in environmental protection as they process and manage organic wastes/residues while producing energy in the form of biogas. Biogas is mainly used in boilers for heat production, in combined heat and electricity (CHP) generators, or it is upgraded to biomethane for use as vehicle fuel or for distribution into the natural gas grid.
Anaerobic digestion facilities will be further incentivized by the EU with the aim of increasing biogas (and biomethane) production to 35 bcm (REPowerEU) by 2030 and 95 bcm by 2050 (EU long term decarbonization strategy). Clearly, financial incentives, strict environmental legislation, development of new technologies and new business models are necessary to achieve these goals.
Anaerobic Digestion Fundamentals
LET OUR EXPERTS GUIDE YOU
Substrate metabolism in an anaerobic digestion facility is performed through the action of enzymes. Enzymes are the catalysts of biochemical reactions and are produced by microorganisms present in anaerobic digestion facilities. They are distinguished into extracellular and intracellular enzymes. The former are function inside the bacterial cells, while the latter are released into their external environment. The concentration and activity of the latter determines the degree of particulate matter bioconversion. Besides, most substrates used in anaerobic digestion facilities (manures, crop residues, food wastes, etc) are characterized by a large fraction of particulate organics.